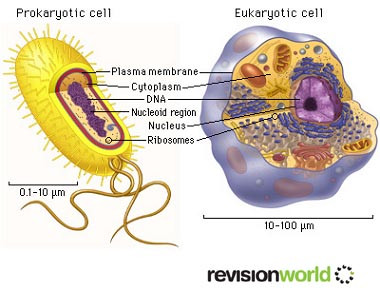
The cell is the smallest unit of life. All living cells contain the following elements:
- plasma membranes - a barrier that controls which substances can pass in and out of the cell, and allows the cell to maintain order
- cytoplasm - the watery jelly in which all the cells reactions occur
- DNA - genetic material that determines which proteins are made and, through enzymes, controls the cells chemical reactions
- ribosomes - organelles that are the site of protein synthesis
- Endoplasmic reticulum - a series of membranes forming a transport system within the cell. Steroid are also synthesised by the ER. Ribosomes may be attached to the ER - this is Rough ER. If no ribosomes are attached it is Smooth ER.
- Golgi apparatus - modified ER that envelopes the products of synthesis in a membrane vesicle to be released by the cell. (eg hormones)
Biggest division between cells:
- prokaryote (no nucleus)
- eukaryote (nucleus)
Common features:
Image
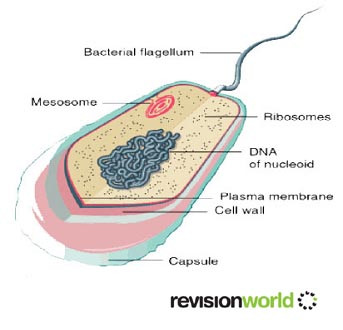
Prokaryotic Cells
- Mesosome – plasma membrane infolding to aid compartmentalisation
- Capsule – sticky outer protective layer
- Cell wall – rigid structure to help maintain shape
- Plasma – separates cell from environment membrane
- Nucleoid – where DNA is found
Image
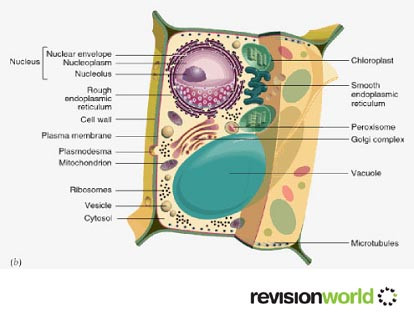
Eukaryotic Cells: Plants
Specific to plant cells:
- Vacuole
- Chloroplast
- Plasmodesma
- Cell wall
Image
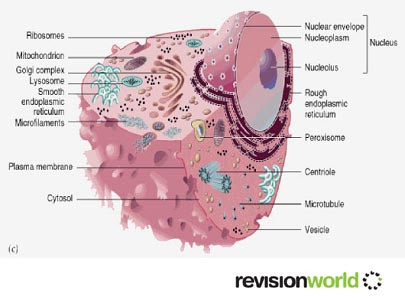
Eukaryotic Cells: Animals
Specific to animal cells:
- Centriole
Image
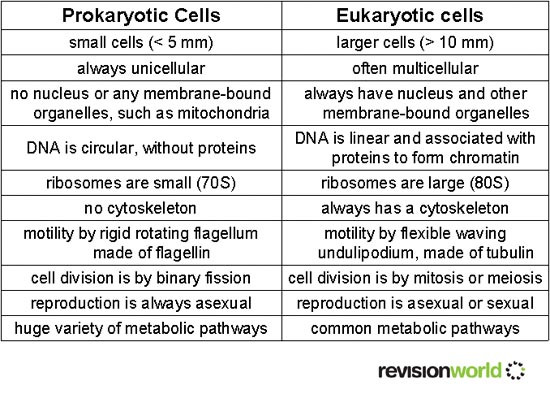
Similarities & Differences
Image