GDP
Gross Domestic Product or GDP measures the value of a nation’s output over a period of time
A nation’s business cycle will display regular fluctuations in economic activity (levels of spending, production and employment) and GDP
Business Cycle Stages
Image
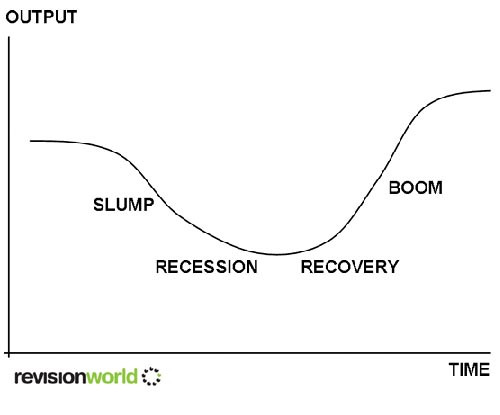
1. Recovery / Upswing
- The economy is recovering from a slump and production and employment is beginning to rise
- Customers are feeling more secure in their employment and are spending more (CONSUMER CONFIDENCE)
- Firms begin to invest more in FIXED ASSETS and increase their capacity
- Increased capacity involves more workers being employed
2. Boom
- Follows the recovery stage
- In this stage production levels are high so employment is also high
- Expenditure from businesses, consumers and the Government increase as confidence grows
- The economy approaches maximum capacity and shortages / bottlenecks occur as raw materials run low
- Skilled workers become scarce and businesses try to attract workers with higher pay
- High wages and scarcity of resources lead to inflation
3. Recession
- The UK Government increases interest rates to curb inflation
- Rising prices of labour and materials mean that businesses costs of production rise significantly and eat into business profits
- Increases in interest rates prevent firms from borrowing and investing money
- Production begins to fall so workers laid off
4. Slump
- Often follows a recession
- Production is low and unemployment is high
- Demand is low
- Governments begin to take action by increasing their own spending to try to create jobs or lowering interest rates to boost demand
