A firms marketing strategy depends on a number of things:
- Its resources
- Their strengths and weaknesses
- Competition
- Skills and assets of the business
- Market opportunities and threats
- Marketing objectives
Marketing Objectives
Marketing objectives are targets that the marketing department wants to achieve. These objectives help businesses achieve their overall objectives. Marketing objectives allow businesses to achieve their marketing strategies.
Examples of objectives:
- - To increase market share by 5%
- - To increase distribution by 4%
Niche Marketing
- Niche marketing is where a business concentrates on a small segment of the market
- This is often used by small companies as it is a way of avoiding competition who may not be interested in such a small segment
- E.g. Gardening magazines, Science fiction books
Mass Marketing
- Mass marketing strategies aim the strategy at the whole market
- This is generally used by larger companies whose products appeal to everyone
- E.g. Ariel washing powder, TV magazines, Bestsellers
Product Differentiation
- This is how businesses make their products stand out from the competition
- They can use USPs – unique selling points to differentiate their products
- By differentiating products you are able to charge a premium price
- Differentiated products are often aimed at specific market segments as they have the features they desire
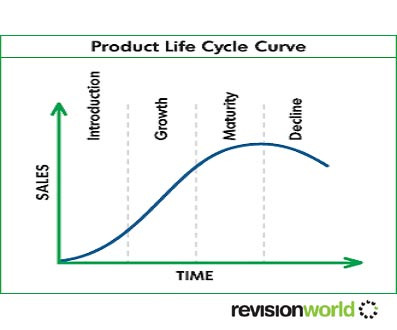
Product Life Cycle
The Product Life Cycle shows the life of a product from its conception to its death
There are five stages in the product life cycle:
- 1. Research and development – the product is being developed, high costs
- 2. Introduction – the product is introduced to the market, sales are low, profit is negative as research and development costs are being met
- 3. Growth – Sales increase rapidly, firm starts to make a profit
- 4. Maturity – Sales reach their peak, profits start to decline as competition increases
- 5. Decline – Sales fall, profits begin to fall, the product might be taken off the market
Product Life Cycle - Extension Strategies
Firms often try and extend the life of their products to stop them going into decline
Extension strategies include:
- Reduce price of product
- Find alternative uses for product
- Increase frequency of use of the product
- Change packaging
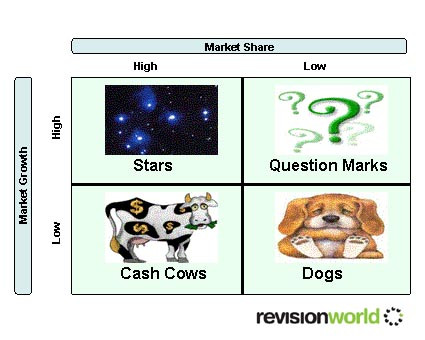
Product Portfolio Analysis
Classifies products according to two dimensions:
- Market growth
- Market share
Organisations aim to have a “balanced portfolio” ideally with cash cows where they can reap the profits and stars that will grow into cash cows
- These tools can be used to analyse the portfolio of products a business offers
- Businesses need to ensure that they have sufficient new products coming onto the market for the future
- New products are funded by profits from products in the maturity phase of the Product Life Cycle (PLC )/ cash cows
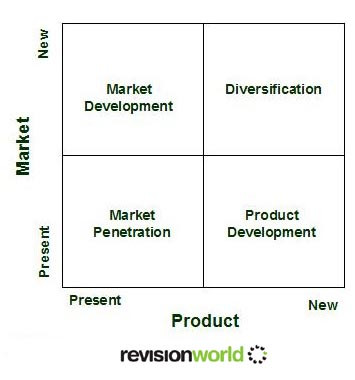
Ansoff Matrix
Four different strategies a business can implement
- 1. Market penetration – sell more products to existing customers
- 2. New product development – sell new products to existing customers
- 3.Market development – sell existing products to new customers
- 4.Differentiation – sell new products to new customers
Experienced Marketing Decision Making
Methods are based on the situation, time available and the managers expertise
Managers make marketing decisions based on:
- Data Hunches
- Scientific Method
- Experience
Scientific Decision Making Method
- Marketing objectives are set
- Data is gathered
- Data is analysed
- Marketing strategy is developed
- Marketing strategy is implemented
- Results are reviewed – this leads back into objectives
