Amines
After studying this section you should be able to:
- explain the relative basicities of ethylamine and phenylamine
- describe the reactions of primary amines with acids to form salts
- describe the formation of phenylamine by reduction of nitrobenzene
- describe the synthesis of an azo-dye from phenylamine
- describe the reactions of amines with halogenoalkanes and acyl chlorides
Aliphatic and aromatic amines

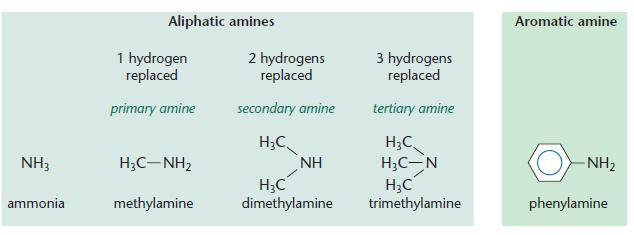
- Notice the similarity with ammonia.
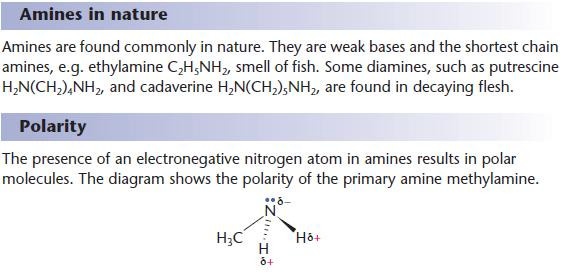
Physical properties of amines
The amino group dominates the physical properties of short-chain amines.
Hydrogen bonding takes place between amine molecules, resulting in:
- higher melting and boiling points than alkanes of comparable relative molecular mass
- solubility in water – amines with fewer than six carbons mix with water in all proportions.
- As with other polar functional groups, the solubility of amines in water decreases with increasing carbon chain length as the non-polar contribution to the molecule becomes more important.
Amines as bases
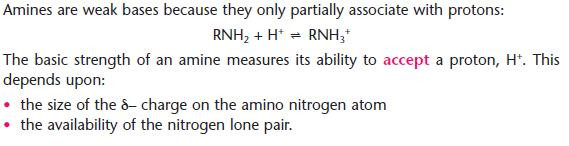
- Amines are the organic bases.
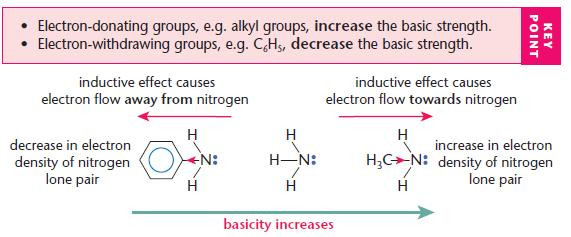
The basicity of aliphatic and aromatic amines
Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia; aromatic amines are substantially weaker.
Organic ammonium salts

- Amines react by the usual ‘base reactions’ producing organic ammonium salts
- A proton, H+, is added to the amino nitrogen atom.
Preparation of amines
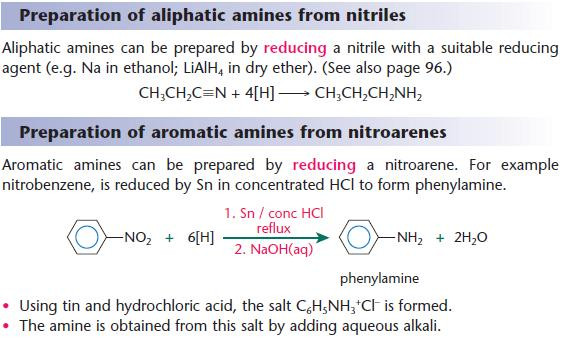
Other reducing agents can also be used:
- H2/Ni catalyst
- LiAlH4 in dry ether
- LiAlH4 is an almost universal reducing agent and works in most examples of organic reduction.
Preparation of amines from amides (Edexcel only)
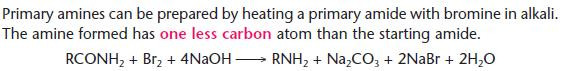
- This process is often called the Hofmann degradation and can be used to move down a homologous series.
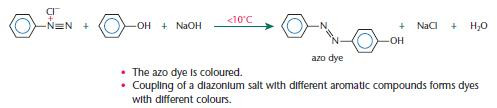
The preparation of dyes from aromatic amines
Aromatic amines, such as phenylamine, are important industrially for the production of dyes. Modern dyes are formed in a two-stage synthesis:
- the aromatic amine is converted into a diazonium salt
- the diazonium salt is coupled with an aromatic compound such as phenol, forming an azo dye.
Formation of diazonium salts
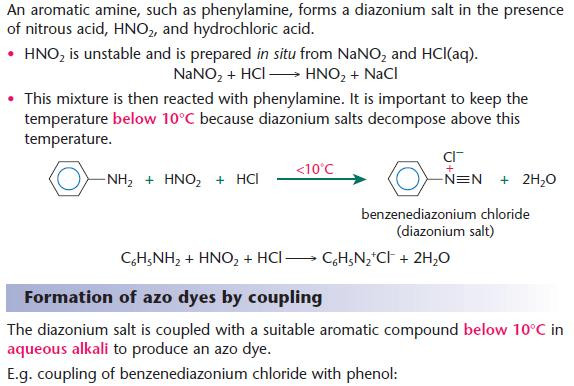
Using benzene for the synthesis of dyes
Benzene is used as the raw material for the synthesis of dyes.
A four-stage synthesis is shown below:
- benzene is nitrated to nitrobenzene
- nitrobenzene is reduced to phenylamine (see above)
- phenylamine is converted into a diazonium salt
- the diazonium salt is coupled with an aromatic compound such as phenol, forming an azo dye.
Reactions of amines with halogenoalkanes
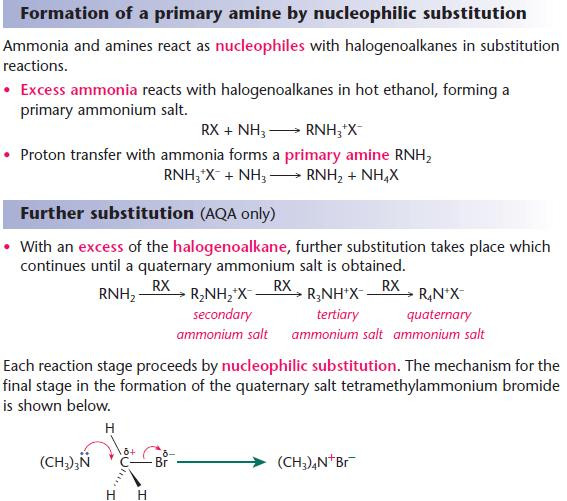
Key points from AS - Nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogenoalkanes
- At each stage, a hydrogen atom is replaced by an alkyl group.
- Quaternary ammonium salts are used as cationic surfactants in fabric softeners.
Reactions of amines with acyl chlorides
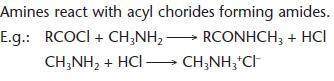
PROGRESS CHECK

