Halogenoalkanes
After studying this section you should be able to:
- understand the nature of the polarity in halogenoalkanes
- describe nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogenoalkanes
- explain the relative rates of hydrolysis of different halogenoalkanes
- describe elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes
- understand that reaction conditions can be used to control the
- products
Halogenoalkanes
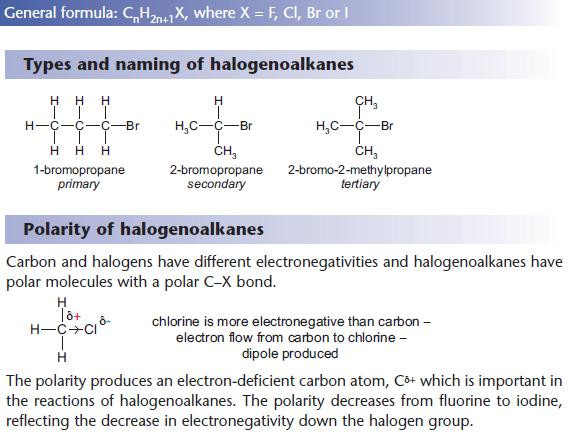

Like alcohols, halogenoalkanes can be primary, secondary or tertiary.
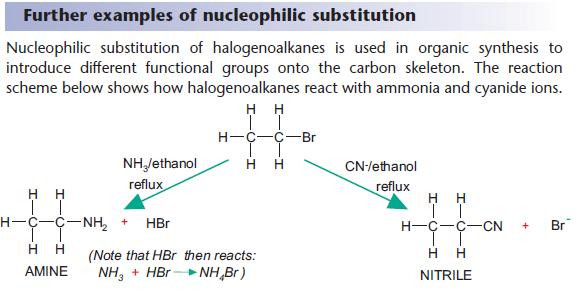
Nucleophilic substitution reactions of halogenoalkanes
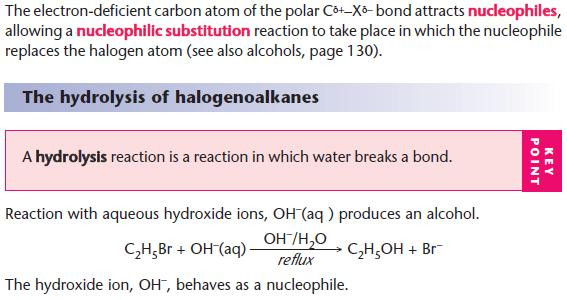
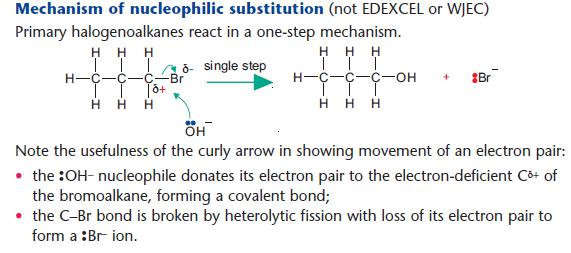
NaOH(aq) is used as a source of OH– (aq).
The OH– ion behaves as a nucleophile by donating an electron pair.
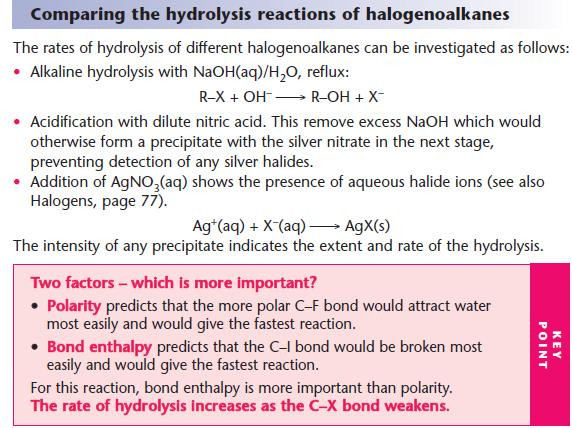
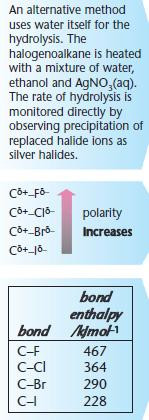
For hydrolysis, water is used as the solvent.
For other nucleophilic substitutions, it is important that water is absent or hydrolysis will take place.
Ethanol is used as the alternative solvent.
Elimination reactions of halogenoalkanes
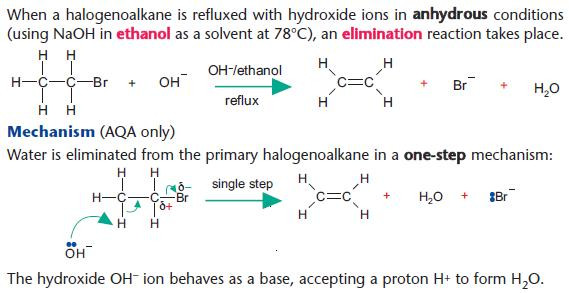
Elimination versus hydrolysis
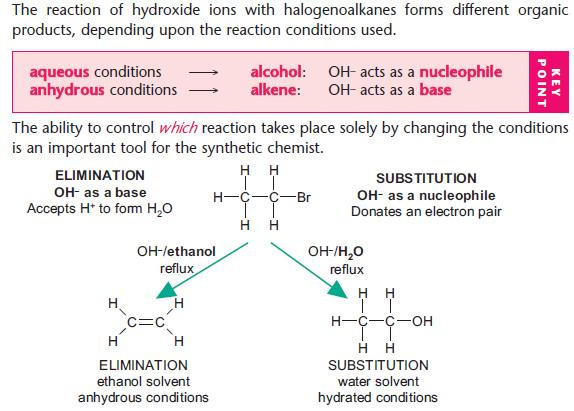
The ability to control:
Use different reaction conditions to control the type of reaction.
The ability to control is commonly tested in exams.
Uses of halogenoalkanes:
Chlorofluorocarbons, CFCs (refrigerants, propellants, blowing polystyrene, dry cleaning, degreasing agents).
Chloroethene and tetrafluroethene to produce the plastics pvc and ptfe.
Halogenoalkanes as synthetic intermediates in chemistry.
Polychlorinated compounds as herbicides.
Progress check