Costs are what a business pays out
Fixed costs
- These do not alter with output.
- Examples – rent, management salaries, rates
- Graphically fixed costs will always be illustrated by a horizontal line
- As output changes fixed costs stay the same
Variable costs
- Alter directly with the business’s level of output
- Examples – fuel, raw materials
- Graphically variable costs will always be a diagonal line from the origin
- As output changes variable alter directly
Total costs
- Are fixed and variable costs added together
- Managers use these figures to make decisions on level of output and prices
Semi variable
- Have a fixed and a variable element
Average Costs
- Average costs are total costs divided by the quantity produced
- ATC / AC = TC / quantity
- Average fixed costs fall when output increases as the fixed costs are spread over more units
- AFC = FC / quantity
Short Run Costs
- In the short run consider fixed and variable costs
- Average total cost line is U-shaped as when diminishing returns start to kick in the average total cost per unit increases
Image
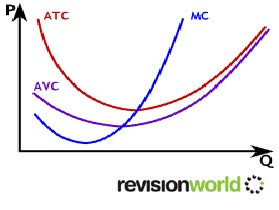
Marginal Costs
- Marginal costs relate to variable costs
- Marginal costs are the amount each additional unit adds to costs
- Marginal costs per unit decrease as production increases until they meet a critical level when they start to increase
Long Run Costs
- In the long run all factors of production can be varied so fixed and variable costs can alter
Technological Change, Costs & Supply in the Long Run
Invention, innovation and technology can impact a businesses by decreasing costs in the long run
Innovation, invention and technology can also impact a businesses method of production – for example causing the firm to move from labour intensive to capital intensive methods
These factors may also result in an increase in efficiency for the firm which can also result in cost savings
