Inflation is the rise in the general level of prices In the long term, inflation erodes consumer purchasing power. That means that accumulated wealth buys less and less, with the passage of time. Where there is high inflation it is difficult for businesses to plan for the future as there is uncertainty regarding the cost of raw materials.
Causes of Inflation
inflation results when the macro economy has too much demand for available production. These alternatives fall under two general categories:
1. Demand-Pull Inflation
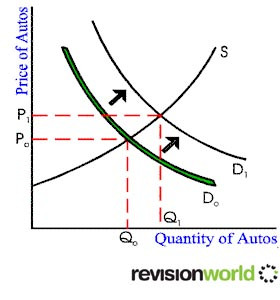
This inflation occurs when household, business, government, and foreign industries collectively try to purchase more output than the economy is capable of producing. In effect, the demand side of the aggregate market is "pulling" the price level higher.
As aggregate demand increases then the general price level rises. When total demand exceeds total supply demand pull inflation occurs.
If the economy is close to full capacity the effects of demand pull inflation will be greater
2. Cost-Push Inflation
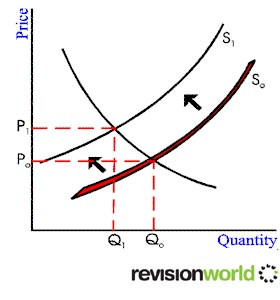
Cost-push inflation is inflation attributable to decreases in supply, primarily due to increases in production cost.As costs rise it causes the aggregate supply curve to shift onwards so less is supplied at each price level.
Each time the aggregate supply curve shifts inwards the price rises causing inflation
Preventing Inflation
One of the best ways to prevent inflation is through stock, variable annuities, and variable universal life insurance. These alternatives provide the potential for returns that exceed inflation over the long term.
Central banks place high interest rates using unemployment and the decline of production to prevent price increases.
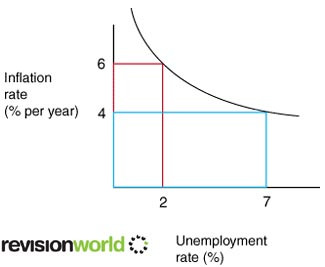
Phillips Curve
Short run phillips curve is curve shaped. The long run phillips curve the curve is vertical.
At this rate the where unemployment is at its natural rate inflation is stable. In the UK since 1997 there has been low inflation and low unemployment