Aggregate supply shows the total amount supplied in the economy as a whole at each price level
In the short term aggregate supply slopes upwards
Image
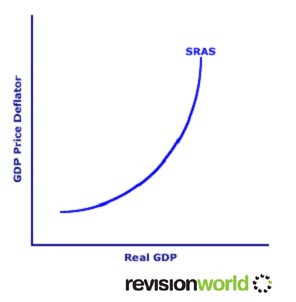
Shifts in the Aggregate Supply Curve
The AS curve may be shifted by changes in:
- The size / quality of the labour force
- The size / quality of capital
- Expectations of inflation
- Technology
- The productivity of labour / capital
- Wages per unit of output
- Taxes / subsidies for producers
The Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve (LRAS)
LRAS is determined by the productive resources available in the economy and the productivity of the factors of production (land, labour and capital)
In the long run the assumption is that supply is not dependent on the level of prices in the economy therefore the LRAS is vertical
- The LRAS is vertical – the same level of income at all price levels
- This is the normal level of output in an economy
- To move the LRAS outwards there needs to be improvements to productivity and efficiency in the economy - this represents economic growth
Image
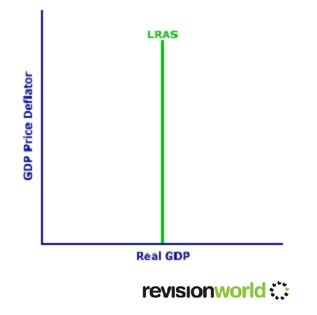
Determinants of Long Run Aggregate Supply Curves
- Technology
- Productivity
- Attitudes
- Enterprise
- Factor mobility
- Institutional structure of the economy
- Economic incentives
