There are a number of types of unemployment:
Structural unemployment:
- This occurs when the economy changes and industries die out
- Training is needed to give the unemployed workers new skills
Cyclical unemployment:
- This is caused by the business cycle
Frictional unemployment:
- This is caused when people are temporarily out of work as they are moving jobs
Unemployment and Business
Increasing levels of unemployment can cause problems for firms.
Cyclical unemployment can lead to a decrease in sales meaning businesses need to look for new markets. Structural unemployment can affect businesses in the local area
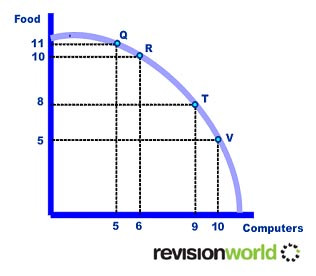
Unemployment & PPF
Unemployment means that scarce economic resources are being wasted reducing the long run potential of the economy. Where there are high levels of unemployment an economy will be operating inside the perimeters of its PPF
Unemployment and Aggregate Demand / Aggregate Supply
As Aggregate demand increases unemployment will decrease. Supply side policies can be used to increase aggregate supply in the economy and thereby reduce the level of unemployment.
However if the growth in the level of aggregate demand is less than the underlying trend growth in output unemployment is likely to occur
Output Gap and Unemployment
The output gap measures the difference between potential and actual GDP.
- If the output gap is high there will be high unemployment and low inflation
- If the output gap is small there is likely to be low unemployment but high inflation as the economy is nearing its productive capacity
