Resistance in Circuits
Series Circuit
R = R1 + R2 + R3 ...
Parallel Circuit
1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 ...
Internal Resistance
A cell in a circuit has its own internal resistance, r. The greater the cell’s current the more work is done against the cell’s internal resistance, and therefore less can be done on the external circuit.
emf = terminal p.d. + p.d. across internal resistance
E = V + Ir
Kirchhoff's Laws
Kirchhoff’s Laws are Conservation Rules of a circuit. Here is detailed video explanation.
1st Law (The Junction Rule): “The total current that enters a junction is equal to the total current that leaves the junction.”
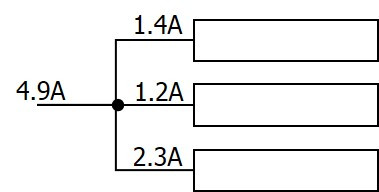
Here, the charge is conserved.
2nd Law (The Closed Loop Rule): Conservation of energy. “Around any closed loop (i.e. complete series path), the total emfs is equal to the sum of the pds."
E = ΣIR
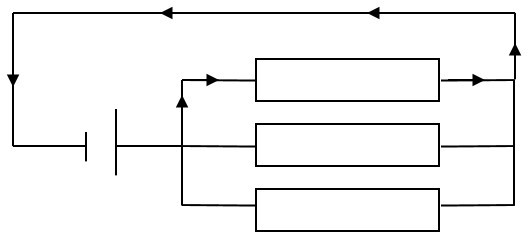
An example of a closed loop
Here, the energy is conserved.
