Particle Exchange
The interaction between particles that results in attractive and repulsive forces is due to continual exchange of exchange particles. They have a short existence on borrowed energy, and are often referred to as virtual particles.
The diagram below is a Feynman Diagram of two electrons interacting. The straight lines show the paths of the electrons, and the squiggly line shows the virtual photons that move between them.
This is an example of the electromagnetic force interactions.
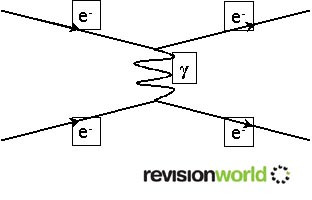
There is a similar interaction for the other forces. For Gravitational Forces, the exchange particles are called gravitons but these haven’t been observed yet.
The Strong Force is what holds quarks together in a nucleon, and their exchange particles are called gluons.
The above Feynman diagrams show the interactions that are responsible for the Strong Force between nucleons. These are called pions or pi-mesons and are some of the Strong Force interactions. The - + 0 represent the charge.
For Weak Force interactions, there is an exchange of one of three kinds of particles called intermediate vector bosons. The symbols for these are W+, W -, Z0 and like pions the - + 0 represent the charge.
The above Feynman diagrams show the neutino-neutron interaction, ?- decay interaction, and the electron-antineutrino collision interaction, respectively.
