Types of Response - CNS
The nervous system is made up of the CNS (Central Nervous System) and the peripheral nervous system.
The CNS is the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is all the nerves passing information to and from the CNS.
Once the information reaches the CNS from a sensory neurone there is a choice:
Either: The message may be passed straight to a motor neurone via a relay neurone. This is very quick and is called a reflex action.
Or: The message can be sent to the higher centres of the brain and the organism might decide to make a response. This is called a voluntary action.
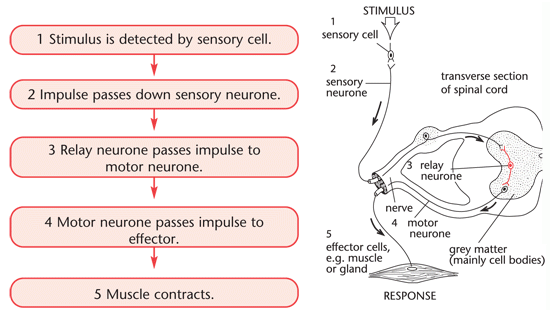
A reflex action
All reflexes are:
- fast
- do not need conscious thought
- protect the body.
All reflexes involve the brain - the pupil reflex govia the brain for example
Examples of reflexes include the knee jerk, pupil reflex, accommodation, ducking and withdrawing the hand from a hot object.
This video explains how reflex actions work
Reflex Arc
A reflex arc is the subconscious movement from a stimulus that can cause harm e.g. a bee sting
The reflex arc does not require a conscious action, which might be too slow
So… the brain is bypassed
Stimulus > receptor > effector > response
A voluntary action
Voluntary actions need a conscious decision in order to take place. They therefore always involve the brain.
The cerebral hemisphere is the area of the brain where the decisions are made. Nerve impulses from here are sent down the spinal cord to effectors via motor neurones.
