Evolution and Extinction
Evolution
Darwin made 4 key observations:
- 1) Living things tend to produce more offspring than survive
- 2) Population numbers in a species stay constant over time
- 3) Each species displays a wide variation in features
- 4) Some of these variations are passed on to offspring
Living things are in continuous competition with each other for food, space, mates
It is ‘Survival of the Fittest’
Natural Selection = Survival of organisms best suited to surviving and reproducing in their environment
This video provides an overview of Darwins impact
Evidence for Evolution
Rocks and Fossils
The remains of organisms from millions of years ago are preserved as fossils in sedimentary rocks
Fossils are formed in one of two ways:
- 1) Organism decomposes, and minerals become implanted in the tissue so that the organism turns to rock
- 2) Organism’s shape leaves an impression in the ground
Fossils are formed in areas of insufficient oxygen to decay, in low temperatures (glaciers) and high soil acidity (peat bog)
This video explains how fossils are used by scientists
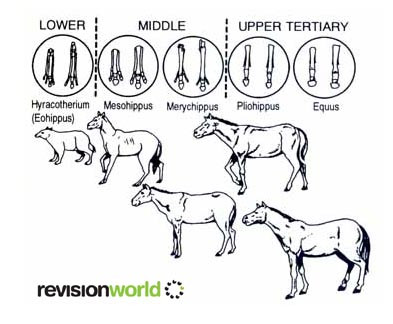
Example of Evolution: The Horse
Fossils provide evidence for the main stages of evolution of the horse over 60 million years
- - Dog-sized to 2m in height
- - Multi-toed feet for walking on forest floor to single-toed hooves for running over open country
Evolutionary Trees
Evolutionary trees are used to represent the relationships between organisms. The diagram shows an evolutionary tree.
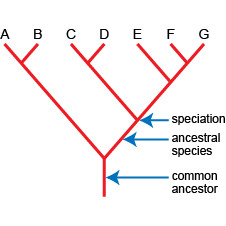
In this evolutionary tree, species A and B share a common ancestor. Species F and G share a common ancestor, which itself shared a common ancestor with species E. All seven species share a common ancestor, probably from the distant past.
Extinction
Species or whole families of organisms die out (extinction)
Any of 3 factors can contribute to extinction:
- 1. environment changes too quickly
- 2. new predator or disease kills them
- 3. beaten by another species for competition for food
Slowly changing environments mean that gradually certain characteristics will become favourable and those species without these characteristics will die out
The environment can also change quickly. This affects great numbers of species that cannot keep up with the changes required for survival.
This video showcases the Extinction threat to the Water Vole
This video explains the Extinction threat to Red Squirrels
