Storing Data, Devices and Media
Data storage devices can be divided into 2 main categories:
Backing storage is used to store programs and data when they are not being used or when a computer is switched off. When programs and data are needed they are copied into main memory but also still remain on backing storage. Magnetic tape drives, floppy disk drives and hard disk drives are all examples of backing storage devices.
The Main Memory contains two types of memory chip called ROM and RAM which hold program instructions and data.
Backing Storage
BITS and BYTES
- Computers store and process data using binary numbers.
- A single unit in binary is called a bit which stands for binary digit.
- Computer memory is measured in bytes. One byte is made up of eight bits.
- One byte can store one character.
The eight bit binary code in this byte represents the letter A
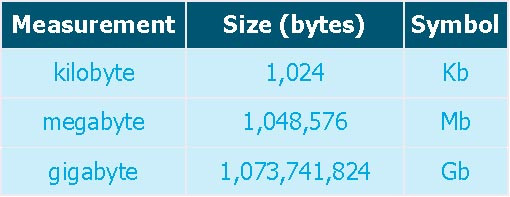
The size of a computer’s memory is normally measured in kilobytes (Kb), megabytes (Mb) or gigabytes (Gb). The table below shows some of the main units of size that we use to measure computer memory.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
- RAM is the computer’s ‘working memory’.
- RAM temporarily stores programs and data that are being used at a given time.
- The contents of RAM can be changed and are lost when the computer is turned off.
- Memory which is wiped clean when the computer is turned off is called volatile memory.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
- The main use of ROM memory chips in a computer is to store the program that runs when the computer is turned on which loads the operating system (e.g. Windows 2000) from disk.
- The contents of ROM can’t be changed and aren’t lost when the computer is switched off.
- Memory which isn't wiped clean when the computer is turned off is called non-volatile memory.
- PROM and EPROM
- PROM and EPROM are both special types of programmable read only memory.
- PROM stands for Programmable Read Only Memory. This type of memory can be programmed once but can’t be changed again afterwards.
- EPROM stands for Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. This type of memory can be programmed and then changed whenever necessary.
Hard Disk Drives
- A hard disk is a circular metal disk coated with magnetic material and usually sealed in a hard disk drive inside the computer.
- Some hard disk drives are not permanently fixed inside the computer but are removable.
- Data stored on a hard disk can be accessed much more quickly than data stored on a floppy disk.
- Hard disks can store much more data than a floppy disk. A typical hard disk inside a personal computer can hold several gigabytes of data.
Floppy Disks
- A floppy disk a circular piece of plastic coated with a magnetic material and protected by a hard plastic cover.
- The size of a floppy disk is measured in inches.
- Modern floppy disks are 3½ inches wide.
The formatting process involves:
- Dividing the surface of the disk into invisible circles called tracks and sectors.
- Setting up a root directory where the list of files that are on the disk will be kept.
- Data on a magnetic disk is located by finding the address of its location from an index in the root directory.
- Each address in the index contains a track and sector number for an individual data segment.
CD-ROM
- CD-ROM stands for compact disk read only memory. A CD-ROM looks just like an ordinary compact disk.
- CD-ROMs can store approximately 650 megabytes of data which is four hundred times more data than an ordinary 3½ inch floppy disk.
- CD-ROM disks come with information already on them and are read only. This means that the information on a CD-ROM cannot be erased or changed, and no new information can be saved.
Writeable CD's
Writeable compact disks are supplied blank and can have data put onto them using a special read/write CD drive.
There are two main types of writeable compact disk;
- WORM (Write-Once, Read-Many) disks which can have data written to them just once.
- Magneto-Optical disks which can have data written to them any number of times just like a hard disk.
Digital versatile disk (DVD)
- DVD is the latest way of storing data
- DVD discs are expected to replace ordinary compact discs and video tapes in the future
- A DVD disc can store up to 17 gigabytes of data. This is enough storage space for at least four full-length feature films!
Magnetic Tape
- Magnetic tape comes in two forms; tape reels, and cassettes or cartridges.
- Large tape reels are used to make backup copies of programs and data on large mainframe computers.
- Cartridges are used to make backup copies of the programs and data on personal computers and networks.
- The main advantage of using magnetic tape as backing storage is that it is relatively cheap and can store large amounts of data.
Direct and serial access
- Floppy disks, hard disks and CDs all allow direct access to data.
- Direct access means that the required data can be found straight away without having to read through all the data on the disk.
- Magnetic tape allows only serial access to data. To locate data on a magnetic tape it has to be searched from the beginning until the required data is found.
File Compression
- File compression software can be used to make files smaller so that more data can be stored in the same amount of space on backing store.
- When a compressed file on backing store needs to be used it must be decompressed.
- This can be done using decompression software or by setting files up to be self-extracting which means that they can automatically decompress themselves.
- Winzip is an example of software that can be used to compress and decompress files.
