Databases
Suppose a school stores information about its students on record cards. Each student has their own card; this is their record.
This video looks at databases
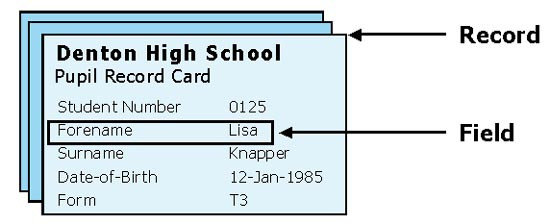
The individual pieces of information recorded on each card, such as name and date of birth, are called fields.
Files, records and fields
- Information in computer-based filing systems is stored in data files. A file is a collection of related records.
- Related records means that each record in a file will contain the same sort of information as all the other records.
- A record must have at least one field. A field contains one individual item of data.
- The arrow below is pointing to the fields, there are four fields in each record of this file
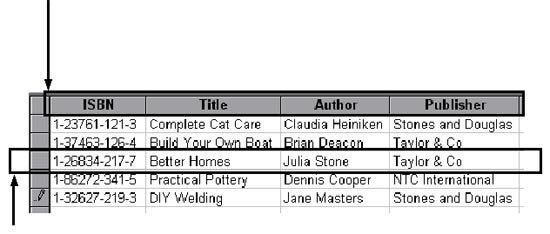
ISBN is the key field. This is the field that has a different value in every record. It is used to distinguish one record from another. A key field uniquely identifies an individual record.
Fixed & variable length records
- A fixed length record is one where the length of the fields in each record has been set to be a certain maximum number of characters long.
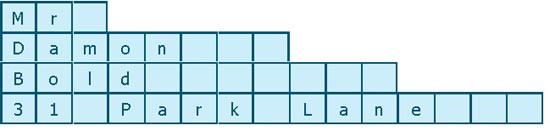
- A set amount of storage space is set aside for each field. If the contents of a field don’t fill the space completely it is remains empty and is wasted.
The problems with fixed length records are:-
- Fields very rarely contains the maximum number of characters allowed which wastes space;
- Values sometimes can’t be entered because they are too large to fit inside the allowed space in a field.
The advantage of fixed length records is that they make file processing much easier because the start and end of each record is always a fixed number of characters apart. This makes it much easier to locate both individual records and fields.
A variable length record is one where the length of a field can change to allow data of any size to fit.
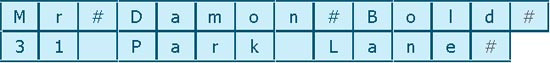
- A special marker (# in this example) indicates where each field ends.
- The length of a field depends upon the data that is placed in it. Only the space needed for a field is ever used — so none is wasted.
- The advantage of variable length records is that space is not wasted, only the space needed is ever used.
- The main problem with variable length records is that it is much more difficult to locate the start and end of individual records and fields.
- To separate variable length records each field has a special character to mark where it ends — called an ‘end-of-field marker’. When records need to be located the computer must count through the end-of-field markers to locate individual records and fields.
Computerised databases
- A database is a structured collection of related data.
- It can be a single file that contains a large number of records or a collection of files.
- Many modern databases are described as being relational.
- A relational database stores data in tables that are linked together using common fields.
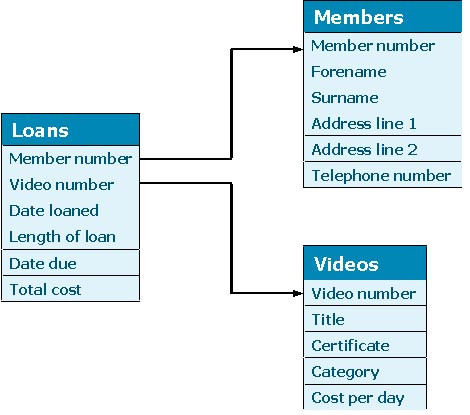
Linked data tables in a relational database
File Operations
- File operations are the different things that can be done to a computer file.
- The main types of file operation are searching, sorting, updating and merging.
Searching
- Searching, or interrogating a file, involves looking for an individual record or group of records that match a certain condition.
- Searches are also called queries.
- To search a database the user must enter a query. The query tells the software which fields to look at in each record and what to look for.
Sorting
- Sorting involves putting the records in a file into a particular order, such as alphabetical order.
Merging
- Merging involves combining two files to produce one new file. This can be done by merging a file of new records to be added with another file that contains all of the existing records — called the master file.
Updating
- The information stored in computer files must be kept up-to-date or it will cause problems for the business or organisation that’s using it.
- To keep a file up-to-date it must be regularly updated. This involves inserting, deleting and amending records.
- When a new record needs to be added to a file, it is inserted. Records are deleted when they are no longer needed. Records are amended when the data in one or more of the fields needs to be altered for some reason.
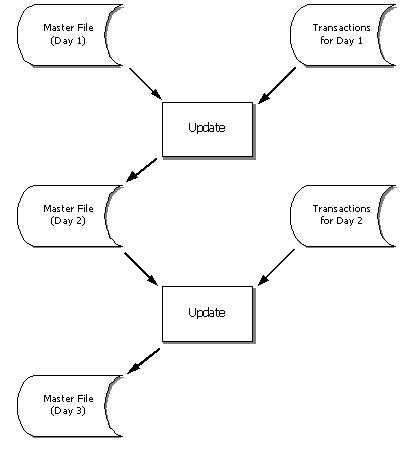
- Details of all the changes that need to be made to a master file are often collected together in a transaction file.
- The master file is updated by comparing it with the transaction file and making changes to any records that appear in both files. Normally at least three ‘generations’ of a master file are kept for backup purposes. If the latest version of the master file is damaged it can be recreated by re-running the previous update using the old master and transaction files.
- The grandfather-father-son method of updating can be seen below.
Backing up online databases
An on-line database is constantly being updated. To make sure no data is lost in the event of hardware failure special back-up methods are used.
Two commonly used methods are:-
- Transaction logging;
- RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks)
RAID is a technology that connects two or more hard drives to improve storage performance and/or to protect against hardware failure. This video explains what RAID is all about.
Database packages
Most databases are set-up using a database package.
A typical database package will allow a user to:
- Create a file by entering their own field definitions;
- Specify automatic validation checks for fields;
- Add new fields to records or delete fields that are no longer needed;
- Add, edit and delete records in a file;
- Perform simple searches and complex searches using more than one condition;
- Import data from other applications software;
- Export data in standard file formats to other applications software;
- Create customised report forms for output;
- Create customised data entry screens;
- Create customised menu screens and link them menu together;
- Link files together using common fields.
