The Muscular System and Movement
The muscular system and skeletal system work in tandem to produce movement, maintain posture, and provide stability for the human body. This collaboration involves muscles, bones, ligaments, and tendons, each playing a crucial role in facilitating and controlling movement.
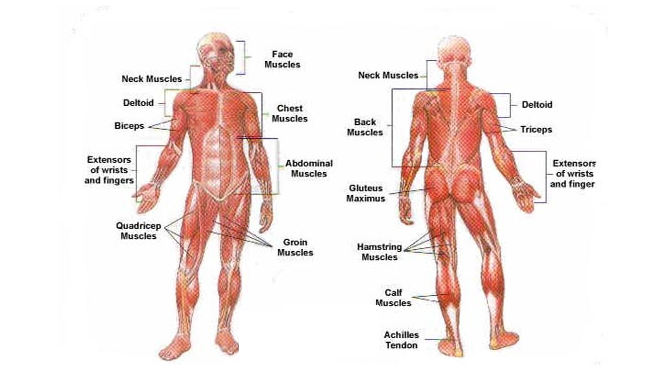
Muscles:
Muscles are the contractile tissues responsible for generating force and causing movement.
They attach to bones via tendons and exert force on the skeleton to produce movement.
Muscles work in pairs or groups, with one muscle contracting (agonist) while its counterpart relaxes (antagonist) to create coordinated movements.
Bones:
Bones serve as the structural framework of the body, providing support and protection for internal organs.
They also act as levers, allowing muscles to exert force and produce movement around joints.
Ligaments:
Ligaments are tough bands of connective tissue that connect bones to other bones at joints.
They provide stability to joints by limiting excessive movement and preventing dislocation.
Ligaments also help in proprioception, providing feedback to the brain about joint position and movement.
Tendons:
Tendons are fibrous cords of connective tissue that attach muscles to bones.
They transmit the force generated by muscles to the bones, allowing movement to occur.
Tendons are strong and flexible, capable of withstanding tension during muscle contraction.
Muscular System and Skeletal System Interaction:
When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendon attached to the bone, causing the bone to move at the joint.
The arrangement of muscles and bones, along with the coordination of muscle contractions, determines the range and direction of movement.
Muscles and bones work together to produce various types of movements, such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
Importance of Coordination:
Proper coordination between the muscular and skeletal systems is essential for efficient movement and injury prevention.
Muscles must contract and relax in a coordinated manner to produce smooth and controlled movements.
Imbalances or weaknesses in muscles, ligaments, or tendons can lead to poor posture, reduced flexibility, and increased risk of injury.
In summary, the muscular system and skeletal system collaborate to produce movement, with muscles generating force and bones providing leverage and support. Ligaments and tendons play crucial roles in stabilising joints and transmitting forces, ensuring smooth and controlled movement of the body and limbs. Understanding this interaction is vital for athletes and individuals aiming to improve their physical performance and overall health.
