Structure of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system is a framework of bones and connective tissues that provide support, protection, and movement for the human body. Understanding its structure and functions is crucial in physical education.
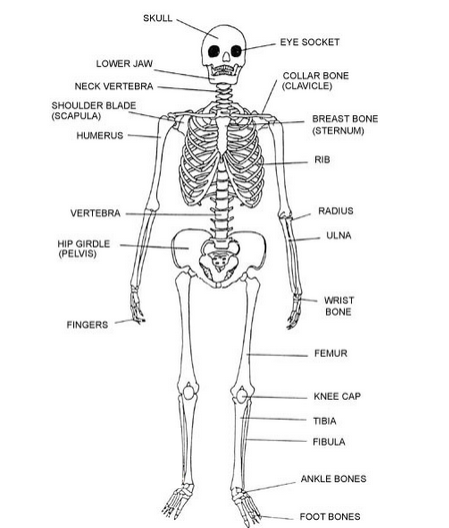
Main Bones of the Skeleton and Their Locations:
Skull:
Located at the top of the body, protecting the brain.
Vertebral Column (Spine):
Runs along the back, providing support and protecting the spinal cord.
Rib Cage:
Encloses and protects the heart, lungs, and other vital organs in the chest.
Pelvis (Hip Bone):
Forms the basin-like structure at the base of the spine, supporting the torso and connecting the spine to the lower limbs.
Upper Limbs:
Includes bones such as the humerus (upper arm), radius and ulna (forearm), carpals (wrist bones), metacarpals (palm bones), and phalanges (finger bones).
Lower Limbs:
Comprises bones like the femur (thigh bone), tibia and fibula (leg bones), tarsals (ankle bones), metatarsals (foot bones), and phalanges (toe bones).
Main Functions of the Skeletal System are:
Support:
The skeletal system provides a structural framework that supports the body's weight and maintains its shape.
Protection:
Bones act as protective shields for delicate internal organs. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the rib cage shields the heart and lungs.
Movement:
Bones, in conjunction with muscles and joints, facilitate movement. Muscles attach to bones via tendons, and when muscles contract, they pull on the bones, causing movement at the joints.
Production of Blood Cells:
Within the bone marrow (found in the cavities of certain bones), red and white blood cells are produced. These cells are vital for oxygen transport, immunity, and overall health.
Mineral Storage:
Bones serve as a reservoir for minerals, primarily calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are essential for various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and maintaining pH balance.
Structural Shape:
The skeletal system gives the body its shape and form. It provides attachment points for muscles, ligaments, and tendons, allowing for coordinated movement and stability.
Understanding the structure and functions of the skeletal system is fundamental in physical education as it provides the basis for learning about movement, injury prevention, and overall physical health.
