Introduction
- Ultrasound is sound with very high frequency
- frequency above 20kHz - inaudible
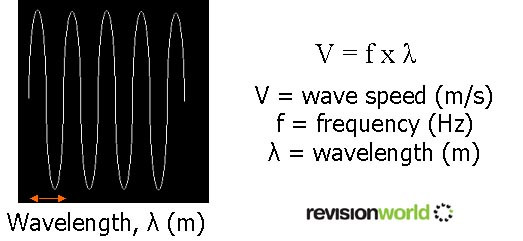
- high frequency = short wavelength
Image
Uses of Ultrasound
1. Industrial Cleaning
- Ultrasound can be used to clean delicate equipment.
- Short ? = narrow, focused beam.
- Vibrations remove dirt effectively by “shaking” dirt loose.
- No need to dismantle the equipment.
2. Industrial Quality Control
- Ultrasound waves can detect cracks inside metals.
- When a sound wave travels from one substance to another, some waves are reflected back as echoes.
- The reflected waves (echoes) are detected by a computer.
- An echo = a flaw in the metal > a crack has formed.
3. Pre-Natal Scanning
- X-rays can be used to see inside the body - (unsafe for a baby)
- Ultrasound can create images and is safer.
- Passes through new substance (skin, muscle, bone) > waves are reflected as echoes.
- The reflected waves (echoes) are detected by a computer.
- These build up a picture from each echo.
4. SONAR
- Bats produce ultrasound squeaks > pick up the reflections using their big ears.
- Brain processes the reflected signals into a mental picture of the surroundings.
- Ships use SONAR to detect items on the seabed.
- The pattern of the reflections indicates the depth and shapes.
