Features produced by Wind Erosion
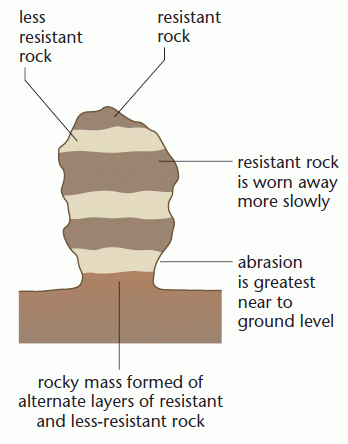
Rock pedestals
Wind sculpts stratified rock into pedestals by wind abrasion and weathering, e.g. Gava Mountains, Saudi Arabia
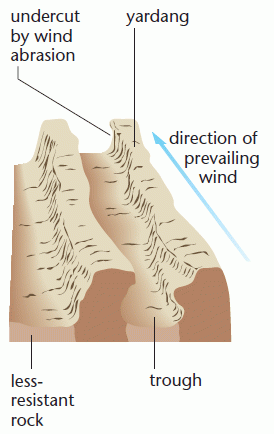
Yardangs (width to depth of 4 : 1)
A ridge and furrow landscape. Wind abrasion concentrates on weak strata; leaving harder material upstanding. The Sphinx at Giza may be a modified yardang!
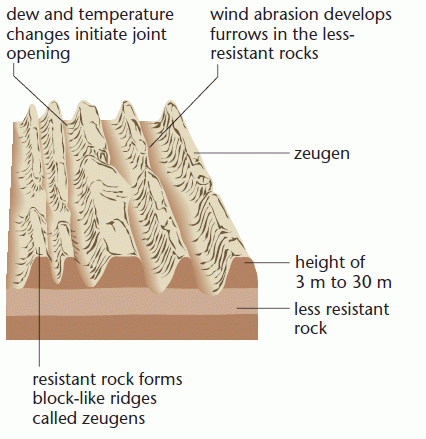
Zeugen
Wind abrasion turns the desert surface into a ridge and furrow landscape, e.g.various areas in Bahrain
Inselbergs
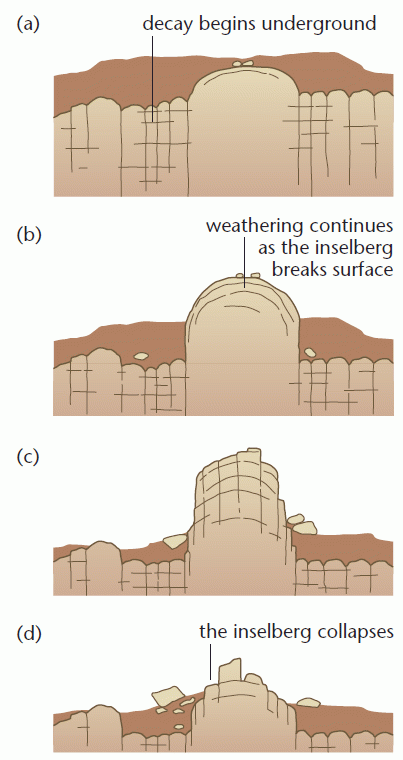
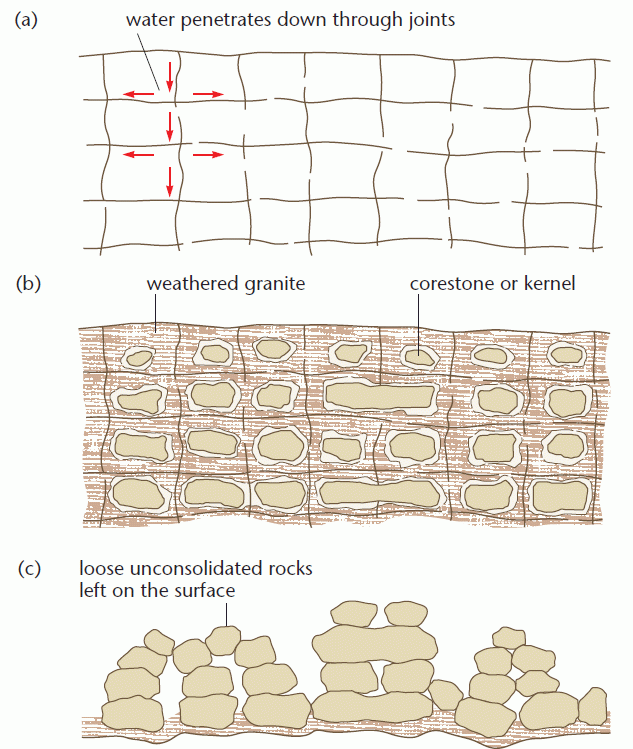
Wind (and water) attacks the original surface leaving round-topped inselbergs (through exhumation). The material removed has a deep-seated ‘decay’ origin and may display extensive ‘unloading’ (subsurface weathering). There are two major forms: domed inselbergs (bornhardts) and boulder inselbergs (Kopjes, rubbins), e.g. Matopos, Zimbabwe
Bornhardt Formation
Kopje Formation
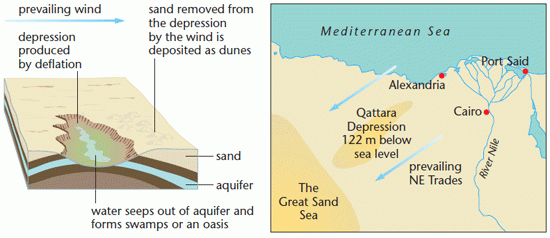
Deflation hollows
These are caused by the removal of fine particles by the wind, lowering the surface and creating a hollow, the best known example is the Qattara Depression.