The Product
Product refers to what the business sells
- This could be a good – tangible or a service – intangible
- Products are composed of different features which help consumers identify them e.g. their size, their colour
- Products need to be developed to meet customer needs and wants
The Product Life Cycle
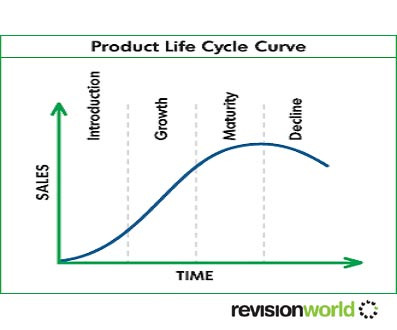
The Product Life Cycle shows the life of a product from its conception to its death
There are five stages in the product life cycle:
- 1. Research and development – the product is being developed, high costs
- 2. Introduction – the product is introduced to the market, sales are low, profit is negative as research and development costs are being met
- 3. Growth – Sales increase rapidly, firm starts to make a profit
- 4. Maturity – Sales reach their peak, profits start to decline as competition increases
- 5. Decline – Sales fall, profits begin to fall, the product might be taken off the market
Extending the Product Life Cycle
Firms often try and extend the life of their products to stop them going into decline
Extension strategies include:
- Reduce price of product
- Find alternative uses for product
- Increase frequency of use of the product
- Change packaging
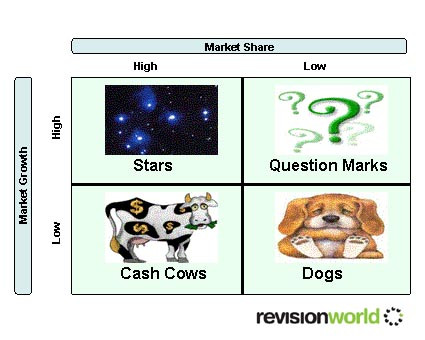
Product Portfolio Analysis
Classifies products according to two dimensions:
- Market growth
- Market share
Organisations aim to have a “balanced portfolio” ideally with cash cows where they can reap the profits and stars that will grow into cash cows
These tools can be used to analyse the portfolio of products a business offers. Businesses need to ensure that they have sufficient new products coming onto the market for the future.
New products are funded by profits from products in the maturity phase of the Product Life Cycle (PLC ) / cash cows