After studying this section you should understand the effect of
- Local Sports Clubs
- Sporting Facilities
- Sporting Bodies & Organisations
Local Sports Clubs
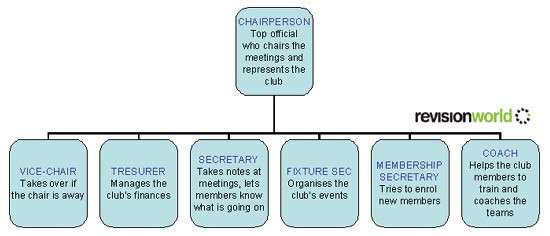
A general structure of a sports club committee, which is elected by the club members
Sporting Facilities
Public Sector Facilities
- Owned by local authorities and councils
- Usually run at a loss
- Sports pitches, leisure centres, swimming pools
Private Sector Facilities
- Owned by companies or individuals
- Run to make money
- Sports stadiums, tennis clubs, golf clubs, health clubs
Centres of Excellence
Offer very good facilities for top class athletes e.g. Crystal Palace, Bisham Abbey, Lilleshall, Holme Pierrepoint , Plas-y-Brenin
Outdoor facilities
Include pitches (football, hockey, cricket), tracks (athletics, horse racing), pools (water sports), courts (tennis, netball) and natural features (canoeing)
Indoor facilities
Usually purpose built buildings, such as swimming pools, sports halls, gyms (used for lots of different activities, like football, badminton, tennis)
Considerations when building an indoor facility
- Are people going to use it?
- Can people park there?
- Can it be used for other things?
- Can people get to it?
- What will it cost?
- Is there any competition?
Sporting Bodies & Organisations
National Governing Bodies of Sport
They have 4 main roles:
- 1. To maintain the rules of the sport and keep the discipline
- 2. To promote the sport
- 3. To organise international competitive events
- 4. To organise national competitions
Examples of governing bodies are the FA (Football Association), UKA (UK Athletics)
Sport England
Aims to:
- Give the UK’s world class performers excellent support
- Improve the UK’s profile and influence on the international stage
- Promote ethical behaviour
- Persuade governing bodies that the UK is the best place to hold major sporting events
